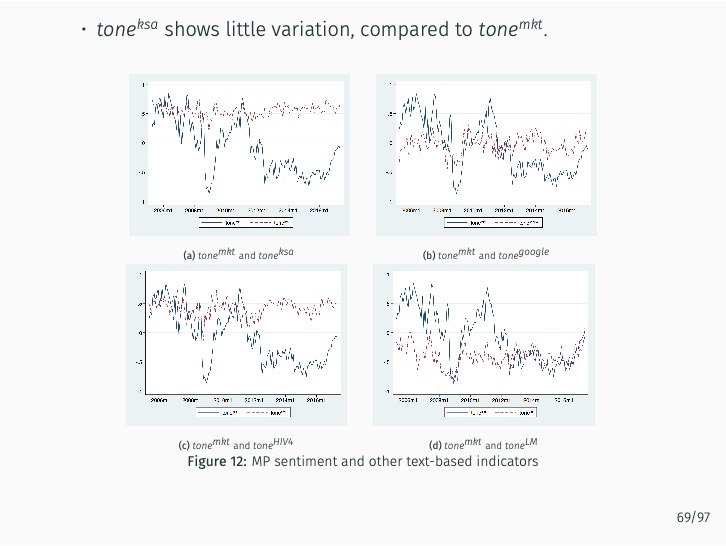
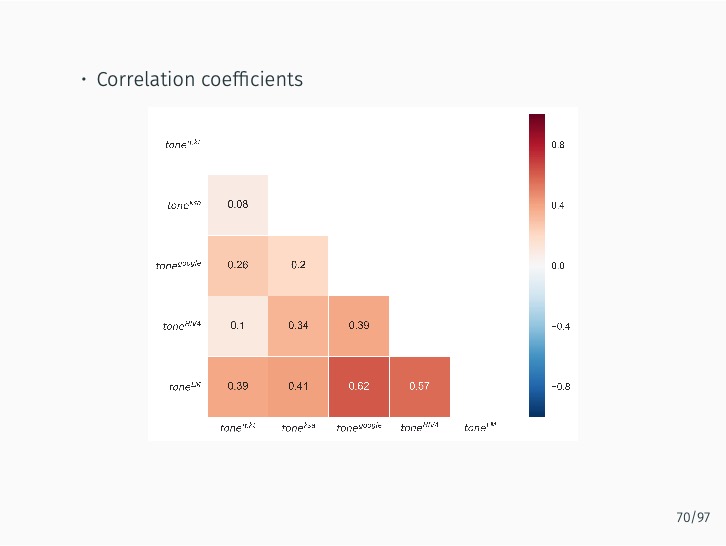
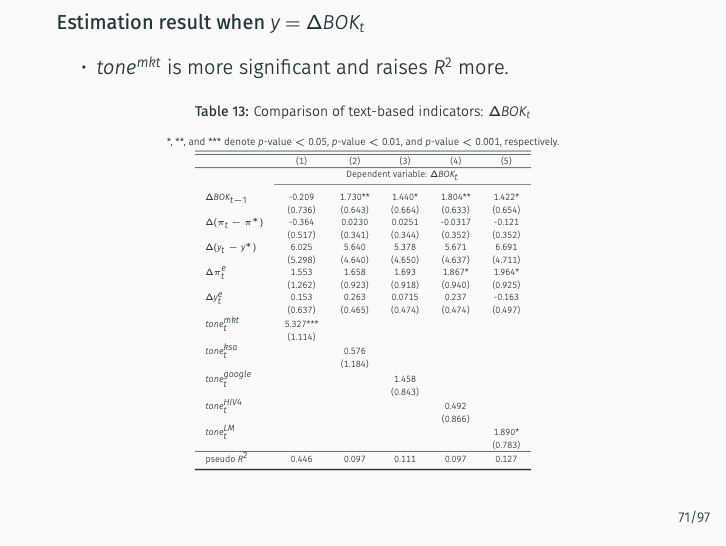
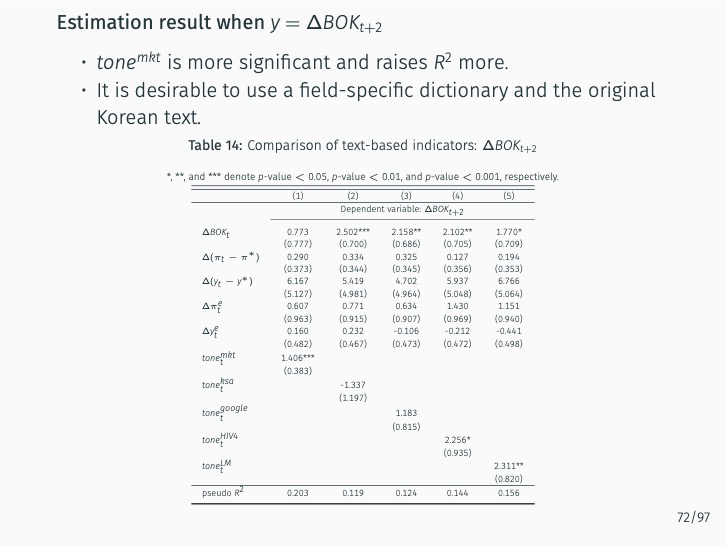
Deciphering Monetary Policy#
Deciphering Monetary Policy with Text Mining: Applying Automated Polarity Classification Approach
Abstract#
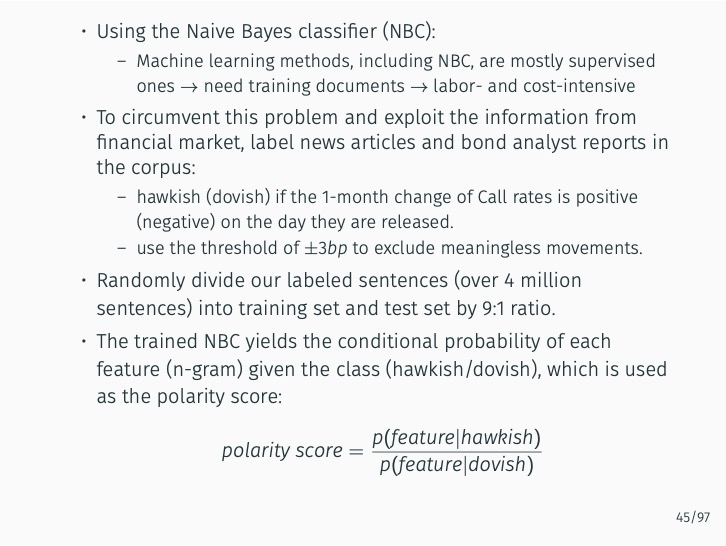
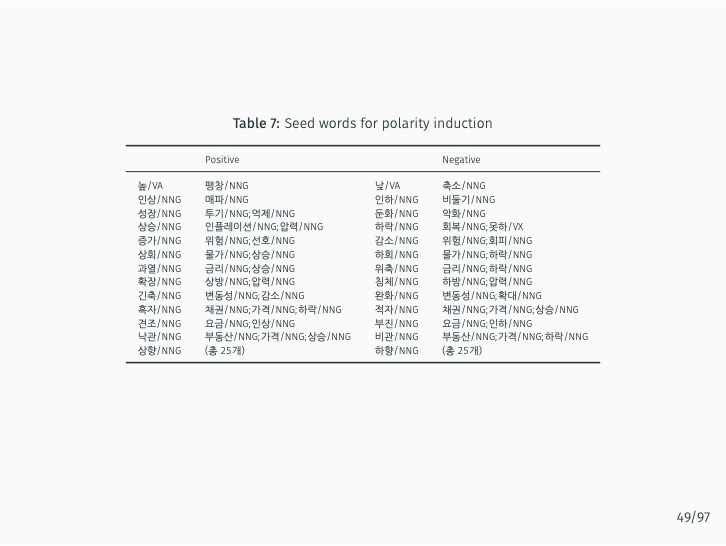
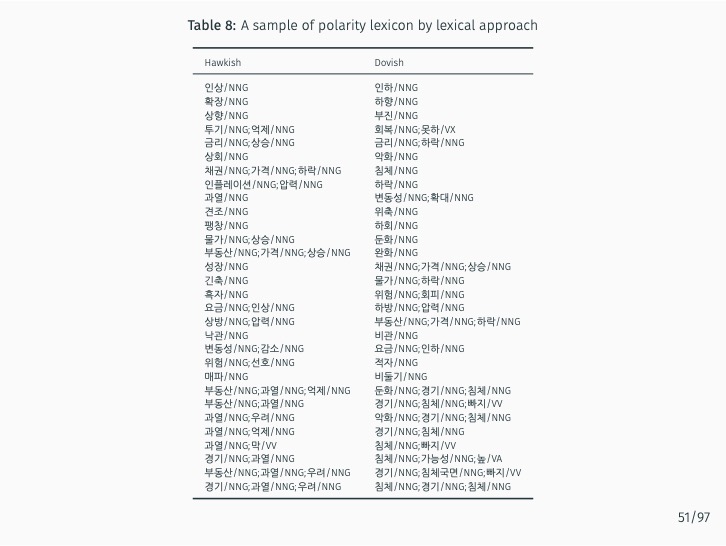
This study introduces two innovative automated methods for creating specialized Korean dictionaries to more effectively gauge the nuances of central bank communication. By utilizing advanced natural language processing (NLP) techniques such as machine learning and word embeddings, as well as a large corpus, these methods classify the hawkish or dovish sentiments of n-grams in an unsupervised manner. To this end, the study presents eKoNLPy [Lee, 2018], a custom NLP library tailored for economic analysis in the Korean language.
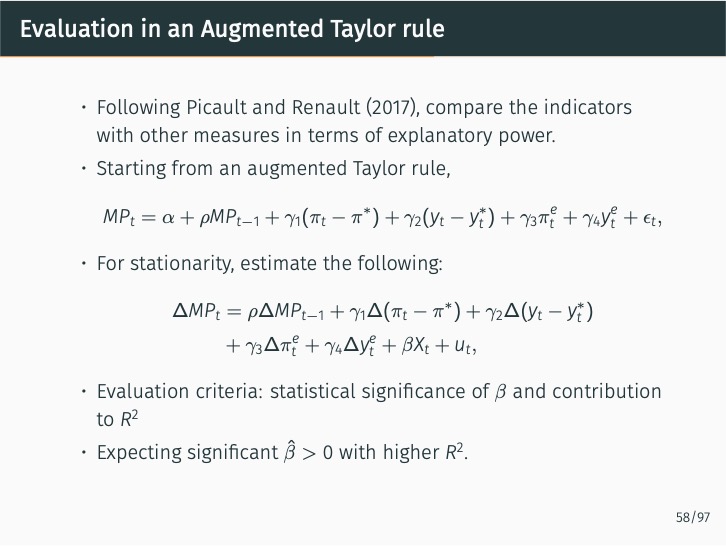
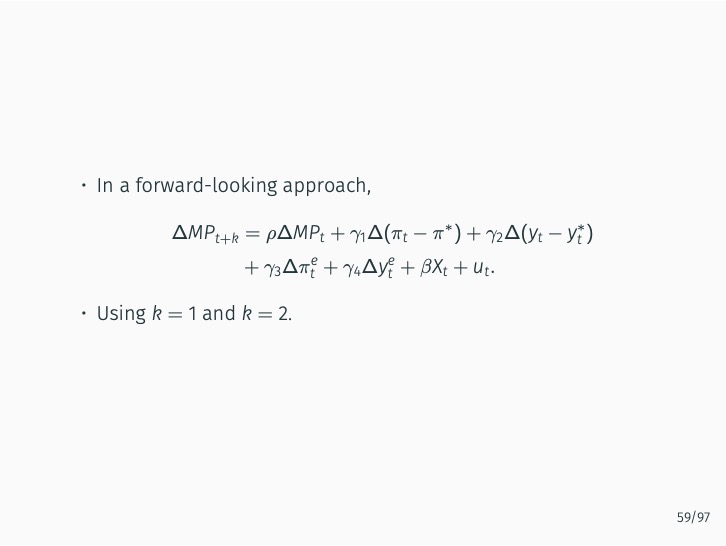
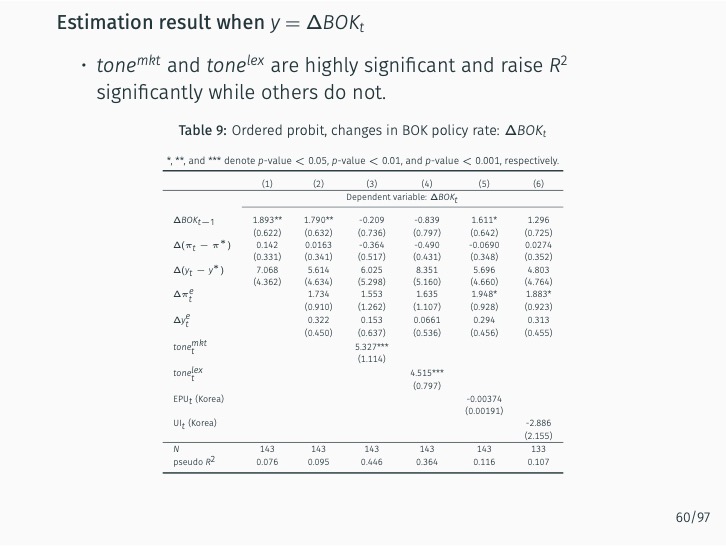
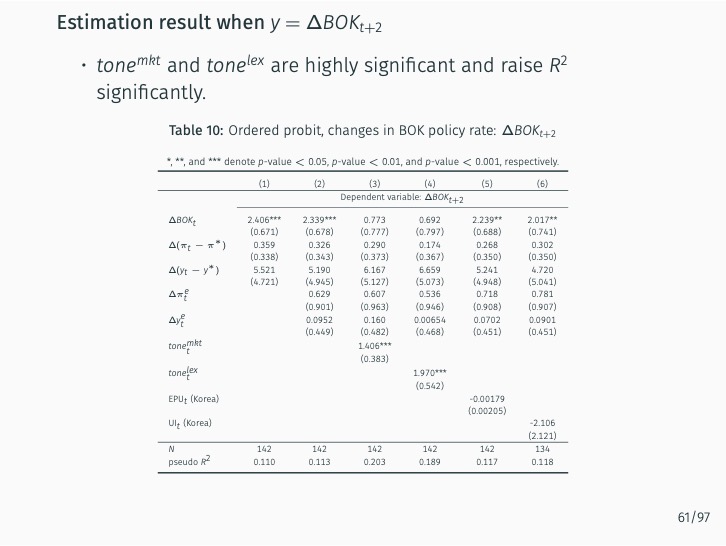
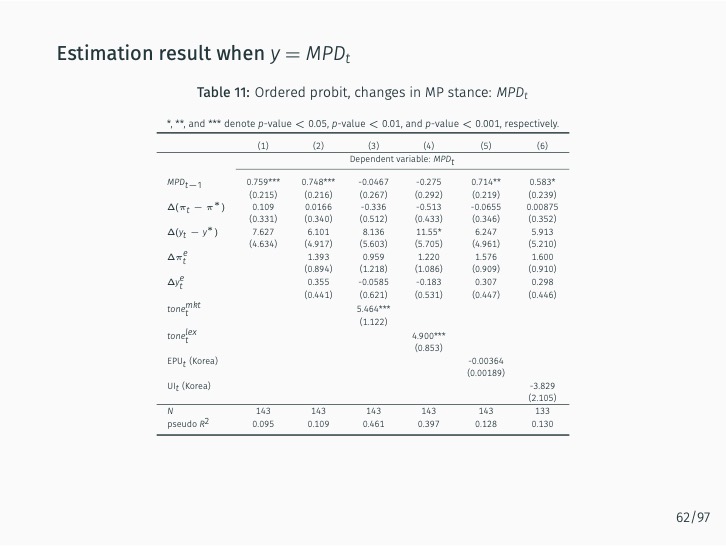
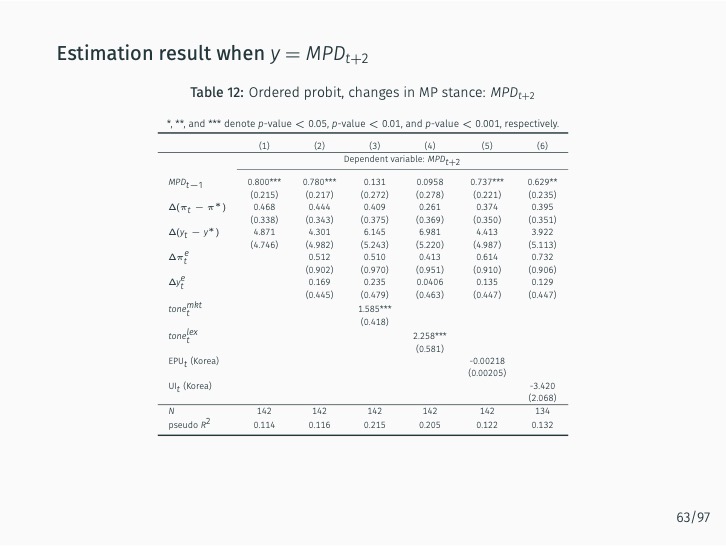
The research demonstrates that lexicon-based indicators contribute to a better understanding of current and future Bank of Korea (BOK) monetary policy decisions when used alongside an augmented Taylor rule. These indicators significantly outperform English-based textual classifications, media-based measures of economic policy uncertainty, and data-based macroeconomic uncertainty measures. The findings stress the value of employing a field-specific dictionary and the original Korean text.
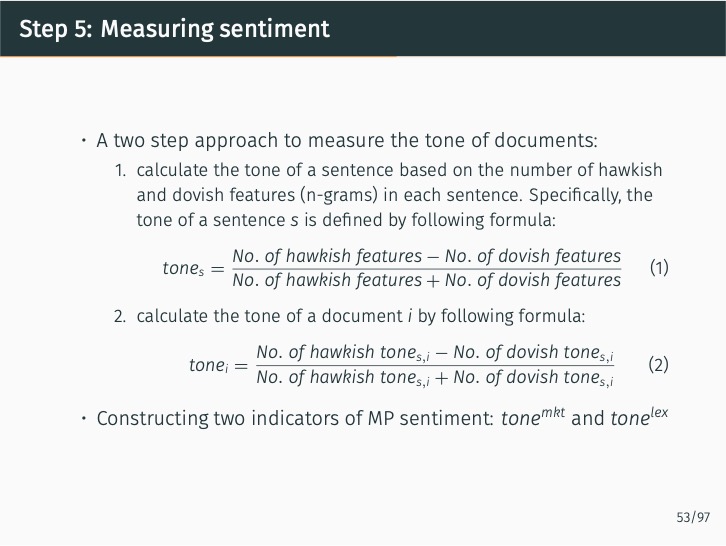
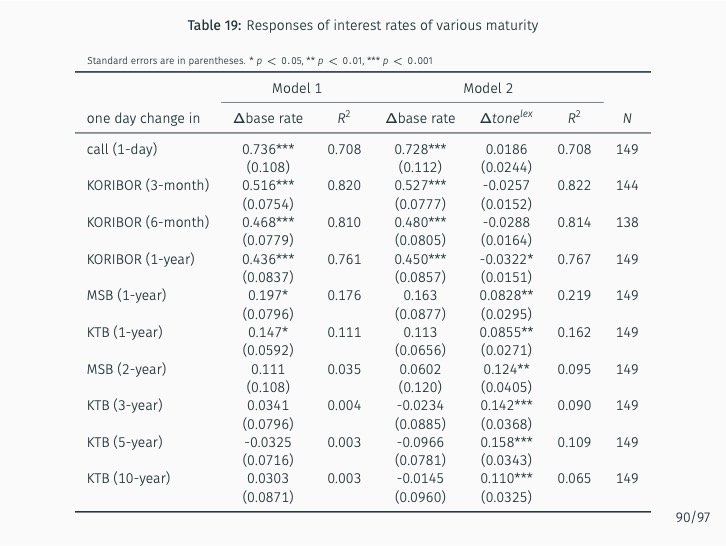
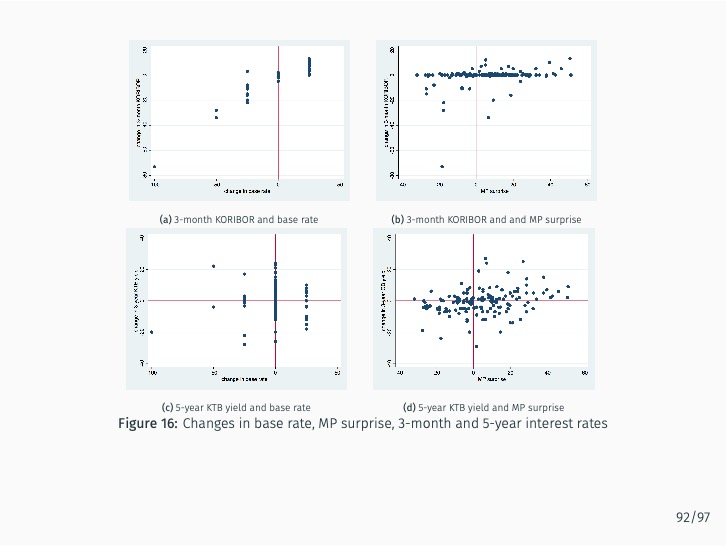
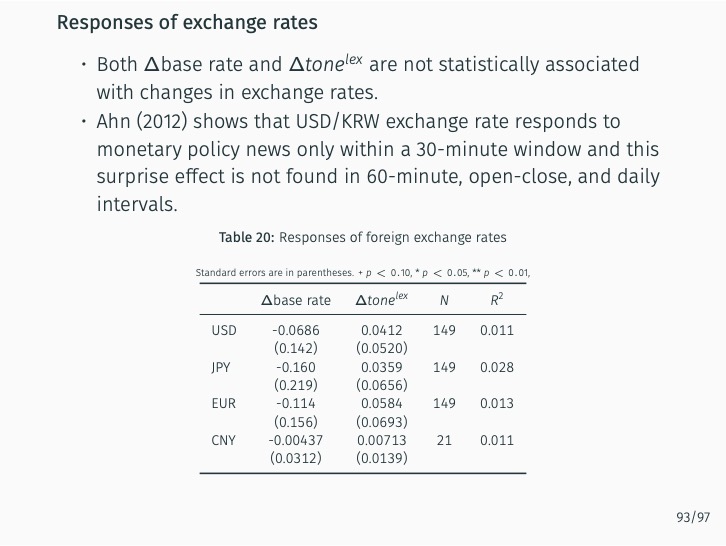
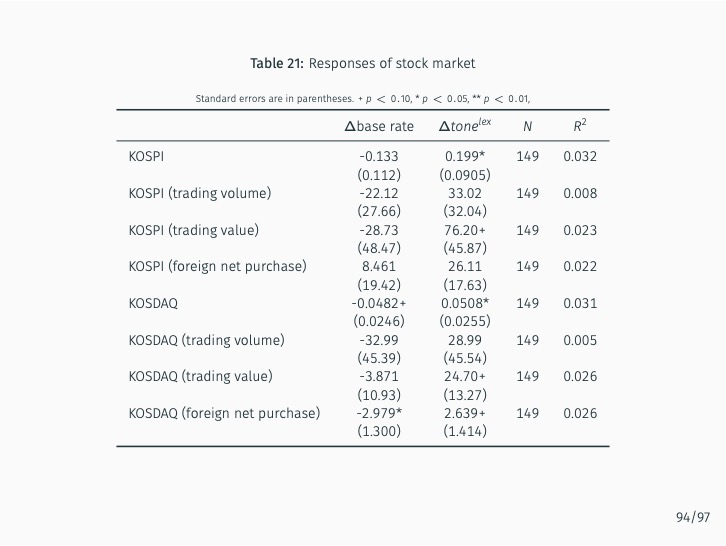
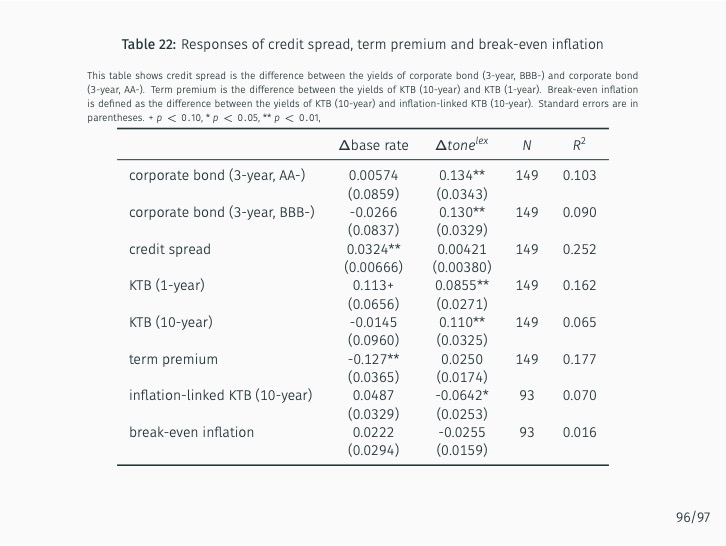
Additionally, the study quantifies the sentiment of news articles surrounding Monetary Policy Committee meetings and measures monetary policy surprises by examining changes in sentiment following policy announcements. The impact of these surprises on various asset prices is then assessed. The study finds that the text-mining-based measure of monetary policy surprise is better at explaining shifts in long-term rates, while changes in the BOK’s base rate are more closely related to fluctuations in short-term rates with maturities of up to one year. This suggests that the text-mining approach accurately captures market expectations of future monetary policy and information related to forward guidance.
References#
Young Joon Lee. eKoNLPy: A Korean NLP Python Library for Economic Analysis. 2018. entelecheia/eKoNLPy.